Tips for Using Devices Safely and Protecting Your Health
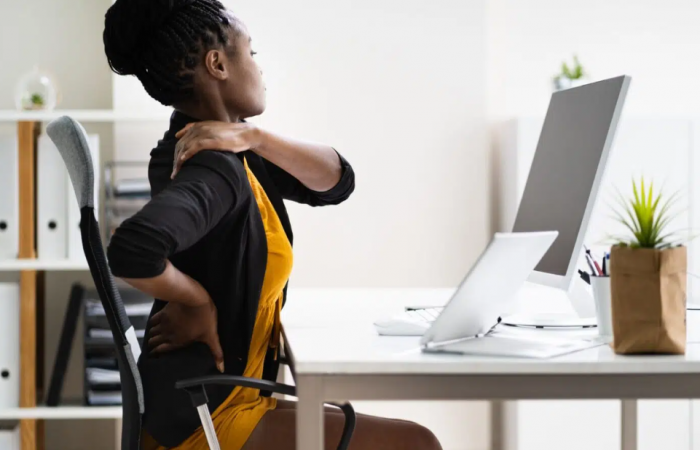
In today's digital age, we spend hours on our devices, tapping away on keyboards, swiping on screens, and gripping phones for hours on end. This tech dependency comes with a physical cost: Repetitive Strain Injury (RSI). Whether you’re working from a laptop, gaming, or constantly on your smartphone, RSI can creep up, causing discomfort and long-term issues. Here’s what you need to know about RSI, its symptoms, and the tips to keep device use comfortable and safe.
What Is RSI?
Repetitive Strain Injury, commonly known as RSI, is a condition caused by repetitive movements or sustained positions that overuse specific muscles, tendons, and nerves. It’s not just a concern for typists or factory workers—anyone who uses devices for long periods can suffer from RSI. Symptoms range from pain, stiffness, and tingling in fingers and wrists to numbness in the shoulders or neck. Left unaddressed, RSI can lead to chronic pain and even difficulty performing basic tasks.

Recognizing RSI Symptoms Early
The key to managing RSI is recognizing it early. Look out for the following signs:
Aching in hands, wrists, or forearms after using devices
Tingling or numbness in fingers
Stiffness in shoulders, neck, or back
Muscle fatigue or weakness in your hands
If you experience these symptoms frequently, it’s time to adjust how you use your devices.
Tips to Avoid RSI When Using Devices
To help prevent RSI, try incorporating these tips into your daily routine:
Maintain Proper Posture: When using a laptop or phone, sit up straight with your shoulders relaxed, and keep your feet flat on the floor. Make sure your head is aligned with your spine to avoid neck strain.
Take Frequent Breaks: The "20-20-20" rule is simple: Every 20 minutes, take a 20-second break and focus on something at least 20 feet away. This not only gives your eyes a rest but also helps you adjust your posture and stretch.
Adjust Your Screen Position: Whether it’s a computer monitor or phone screen, position it at eye level. This helps keep your head and neck aligned, reducing strain on your neck and shoulders.
Use Ergonomic Tools: Invest in ergonomic keyboards, mouse pads with wrist support, and even a standing desk if possible. Ergonomic tools are designed to encourage natural hand and wrist positions, reducing strain during extended device use.
Reduce Grip Pressure: Try not to hold your smartphone too tightly or tap too hard on touchscreens. Excessive pressure and gripping can strain hand muscles, especially with prolonged use.
Position Your Hands Properly on the Keyboard and Mouse: Your wrists should stay in a neutral position (not bent up or down), and your elbows should be close to your body at a 90-degree angle. This helps minimize strain on your wrists and forearms.
Use Voice Assistants or Dictation Features: Typing constantly can strain your wrists, so take advantage of voice-to-text options for emails, texts, and even note-taking. Siri, Google Assistant, and other AI tools can help you cut down on unnecessary typing.
Stretch and Strengthen Regularly: Gentle stretches for your fingers, wrists, and forearms throughout the day can help alleviate muscle stiffness. Exercises such as wrist flexor and extensor stretches, thumb stretches, and shoulder shrugs can all aid in maintaining flexibility.
Invest in a Trackpad or Stylus: Using a trackpad or stylus, especially for design work or extensive scrolling, can reduce repetitive clicking motions and distribute pressure more evenly across your hand and wrist.
Limit Smartphone Usage: If you’re using your phone for prolonged activities, try switching to a computer if possible, as phones encourage cramped hand positions. Texting and scrolling are better suited for larger devices with more ergonomic options.
![]()
Incorporating Device-Free Time into Your Routine
Modern life makes device-free time challenging, but it’s worth it for your health. Try to schedule device-free periods during your day—meal times, breaks, or before bed are excellent options. This helps your hands and wrists recover while giving your eyes and mind a well-deserved rest.
Seeking Help If Pain Persists
If you experience consistent pain despite following these tips, consider seeing a medical professional. Physiotherapists and occupational therapists specialize in treatments for RSI and can provide exercises and therapies to reduce pain and improve strength and flexibility.
Final Thoughts
Technology has transformed our lives, but it shouldn’t compromise our physical well-being. Taking steps to prevent RSI through good habits, ergonomic adjustments, and frequent breaks can save you from discomfort and help you use your devices safely. Remember, it’s easier to avoid RSI than to treat it—so start protecting your health today and make your device use pain-free!